11+ dicot root diagram
Simple vocab like root sprout and seedling. Thus the stem tip two cotyledons feeder root tip and root cap are the parts of a mature embryo.
Important Questions Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy Of Flowering Plants
The Root Cap Primary Roots Lateral Roots 540 Nitrogen Fixation.
. Arrows of the label should point to the part of the diagram and should not overlap each other. The count of parts in a dicot flower is a multiple of four or five or equal to four or five. Apical At or on the apex of a.
They have a fibrous root system. Seed Sorting from Montessori Nature. In monocot flowers the count of parts of the flower is a multiple of three or equal to three.
Create living art with. Onion peel to study the plant cell 12. This page provides a glossary of plant morphologyBotanists and other biologists who study plant morphology use a number of different terms to classify and identify plant organs and parts that can be observed using no more than a handheld magnifying lens.
They have a tap root system. Significance to Plants and Humans 554. Germination is usually the growth of a plant contained within a seed.
NCERT Solutions For Class 11. This page provides help in understanding the numerous other pages describing plants by their various taxa. Of monocot and dicot root Spotting 15.
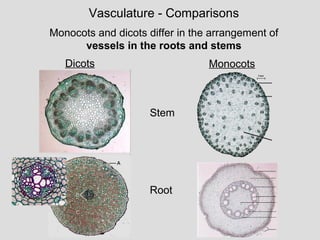
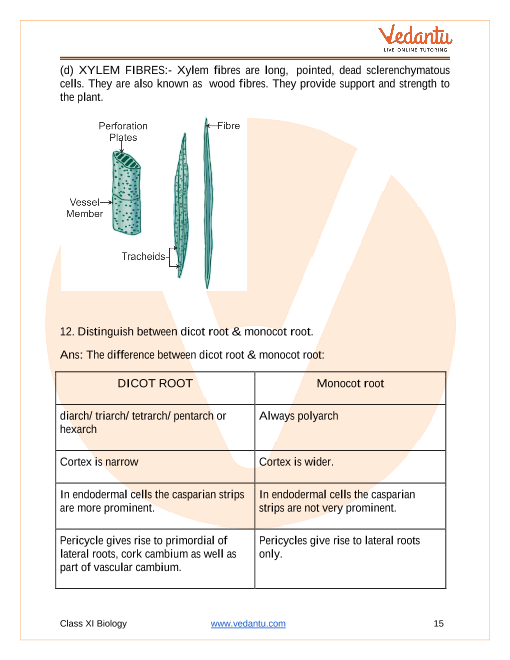
Monocot and Dicot Roots. The classifications like taproots fibrous roots and adventitious roots are elaborated. Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits and form the clade Angiospermae ˌ æ n dʒ i ə ˈ s p ɜːr m iː commonly called angiospermsThe term angiosperm is derived from the Greek words angeion container vessel and sperma seed and refers to those plants that produce their seeds enclosed within a fruitThey are by far the most diverse group of land.
170 and reveals following tissues from outside. Solutions are crafted by a team of experts at BYJUS having extensive knowledge in their. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants is the sixth chapter categorized under unit 2 Structural Organization in plants and animalsNCERT Solutions for Class 11 supplies students with just the perfect tool for learning as well as last-minute reference.
The point furthest from the point of attachment. The difference between dicot and monocot roots is that monocot roots are fibrous roots they have a wide network of thin roots that emerges from the stemDicots on the other hand have taproots which means that they form a single thick root from which small lateral branches emerge. The feeder is a protuberance-like structure present in between root and stem tips.
It is also the process of reactivation of metabolic machinery of the seed resulting in the emergence of radicle and plumule. They hang vertically downward from an aerial branch of a plant. It results in the formation of the seedling.
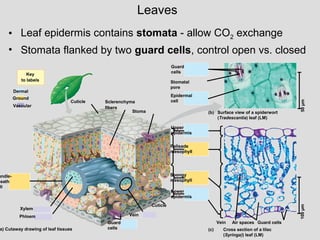
To secure phosphorus P from soil most land plants use a direct phosphate uptake pathway via root hairs and epidermis and an indirect phosphate uptake pathway via mycorrhizal symbiosis. Aphananthous of flowers Inconspicuous or unshowy as opposed to phaneranthous or showy. Leaves in monocots have parallel venation.
A feeder develops after the formation of stem and root tips Fig. Check out this time-lapse video that shows the fascinating details of how a plants root system grows quickly over the course of a few days. These are pillar-like roots.
The characteristics that differentiate angiosperms from gymnosperms include flowers fruits and. Primary Root Tissue Root Hairs and the Plant Vascular Cylinder 645 Root System Growth. - Portulaca and Vitis.
Cells are the basic building block of all living things. Based upon their location and function differentiate amongst the three types of meristematic tissues. Among the plant lineage bryophytes including liverworts mosses and hornworts have relatively simple body structures and are acknowledged for their extraordinary regeneration efficiency because fully differentiated tissue cells can be reprogrammed to stem cells within 2 days after injury 8 9Among the liverworts Marchantia polymorpha represents an emerging.
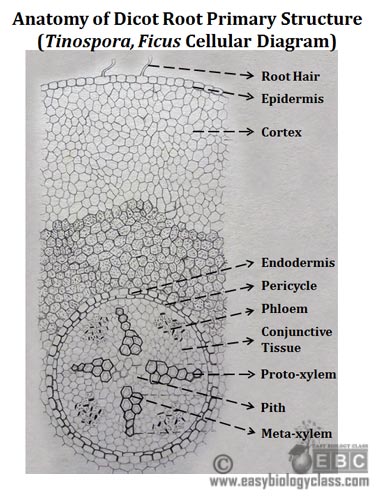
Anatomy of Dicotyledonous Roots. Fibrous roots on the other hand are bushy roots in which thin moderately branching roots grow from the stem. Depending upon the region of occurrence meristems are of three typesapical intercalary and lateral.
The tap root and its branches constitute the tap root system. Anatomy of Monocot Root. Based on the constructed phylogenetic tree and the fixage times of monocot-dicot split time.
Angiosperms also called flowering plants have seeds that are enclosed within an ovary usually a fruit while gymnosperms have no flowers or fruits and have unenclosed or naked seeds on the surface of scales or leaves. Of monocot and dicot stem 14. In higher plants the sink organs such as flowers fruits and seeds are heterotrophic in nature and rely on nutrients supplied from the photosynthetically active organs eg leaves termed source organs for their growth and development 14Higher plants utilize the phloem sieve elements for long-distance transport of nutrients mainly sucrose from the source to the sink organs.
In dicot plants the tap root is persistent and produces lateral roots such as secondary roots tertiary roots etc. The detailed diagram with the genomic context was shown in Supplementary Fig. Place where the meristematic activity takes place.
- The roots are short and grow obliquely from near the base of the main stem. It is circular in outline Fig. Stages of mitosis in onion root tips 13.
Also read Anatomy of Monocot and Dicot Plants. Gymnosperm seeds are often configured as cones. Explore cell definition cell structure types of cells cell theory cell discovery and cell functions BYJUS.
Younger roots towards apex and older roots towards base. Here we mapped a network between transcription factors and mycorrhizal symbiosis-related genes using Y1H. First the topics of the root systems are covered.
Normally dicots and monocots differ in four aspects which include stems flowers leaves and roots. The main difference between monocot and dicot root is that the dicot root contains xylem in the middle and phloem. Unlike in animals in which hormone.
The interaction between these two pathways is unclear. Leaves in dicots have reticulate or net venation. On the basis of the number of cotyledons vascular plants have been.
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics. Draw a diagram to show the location of the three tissues in a plant. Plant hormone or phytohormones are signal molecules produced within plants that occur in extremely low concentrationsPlant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development from embryogenesis the regulation of organ size pathogen defense stress tolerance and through to reproductive development.
Aphlebiae Imperfect or irregular leaf endings commonly found on ferns and fossils of ferns from the Carboniferous Period. The following points highlight the top two types of monocot and dicot roots. These plant roots have a comparatively wider and fibrous root-like structure.
All lateral roots arise in acropetal succession ie. Next the different root regions are discussed in Chapter 5 Class 11 Biology Notes. Anatomy of Dicotyledonous Roots 2.
These roots have swollen parts that appear at regular intervals. The seed of a vascular plant is a small package produced in a fruit or cone after the union of male and female reproductive cells. Older students can tackle advanced terms like cotyledon monocot and dicot.
These plant roots have a comparatively narrow and tap root-like structure. On the opposite side develop the root tip with a root cap.
Plant Structure Growth Development

How To Draw T S Of A Dicot Root Diagram Of Dicot Root Internal Structure Of Dicot Root Youtube
Dicot Root Cross Section Structure Ppt Easy Biology Class

Diagram Of Dicot Root Labelled Diagram Of Dicot Root Class 11 Biology Youtube Root Diagram Biology Diagrams Diagram

Contractile Vacuole Function Role What Is A Contractile Vacuole Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
What Is Lignification What Is The Function Of It Quora

2017 Amep Catalog Science And Math By Ck Sales Associates Llc Issuu
Important Questions Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy Of Flowering Plants

How To Draw Internal Structure Of Dicot Root Easy Way Anatomy In Details Youtube

Cbse Diagrams For Class 11 Biology Important For Exams
Plant Structure Growth Development
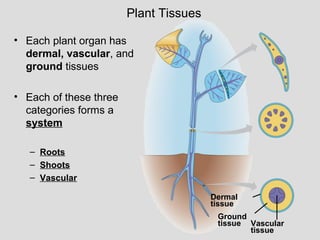
Plant Structure Growth Development

Diagram Of Monocot Root Labelled Diagram Of Monocot Root Class 11 Biology Youtube Root Diagram Biology Diagrams Root

Opal Diagram Dicot Root Youtube

Anatomy Of Dicot Root Class 11th Youtube

Diagram Showing Dicot Roots Structure Stock Vector Illustration Of Vector Background 168896814
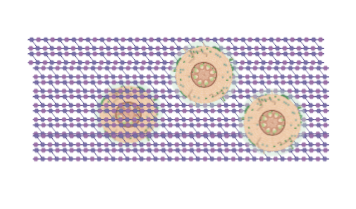
The Given Diagram Is The Anatomy Of A Dicot Root B Class 11 Biology Cbse